The amazing power of Y-DNA can help you break through brick walls in many of your ancestral lines. For example, when there are several men with similar surnames who lived in the same location, it is can be very frustrating to attempt to determine their true relationship.
But Y-DNA can point us in the right direction and can even prove our theories.
You don't have to depend on your own Y-DNA or the Y-DNA of close relatives. I try to track down direct male descendants of all of my ancestral lines to see what Y-DNA can do.
You don't have to depend on your own Y-DNA or the Y-DNA of close relatives. I try to track down direct male descendants of all of my ancestral lines to see what Y-DNA can do.
Since the Y-chromosome is passed from father to son, I need to find a man who is my ancestor's son's son's son . . . . If the surname remained unchanged the descendant will be carrying the surname. This time I want to find more about my maternal grandmother's ancestors.
My problem was particularly troublesome because I am descended from two
men named Michael Kerns (spelled Carn, Carnes, Karns, Karnes, Kern, etc. in the various records) who both lived in Bedford County, Virginia. One died 1807 in Bedford County, and the other left Virginia and died 1814 in Knox
County, Tennessee.
The daughter of Michael of Bedford married the son of Michael of Knox, so that's why I descend from both of them. Genealogists have confused the two men for decades and have placed them in multiple lineages.
Researching in Colonial Virginia is difficult, and deeds are your most important resource for this time period. So years ago I went through all of the deeds of the two Michael Karnes, and I now know where each man lived and have determined the children of both men.
But I
want to find their fathers. Y-DNA testing can be a great way to do this.
If you are relatively new to Y-DNA testing, you may wish to review this post: Y-DNA STRs, SNPs, and Haplogroups. The page will open in a new window, so you won't lose your place here.
If you are relatively new to Y-DNA testing, you may wish to review this post: Y-DNA STRs, SNPs, and Haplogroups. The page will open in a new window, so you won't lose your place here.
EXAMINING STR RESULTS
I found men who were willing to take DNA tests and ordered Y-DNA
tests from Family Tree DNA (FTDNA) for two descendants of Michael Karnes of Knox
County, and one for Michael of Bedford. This test is an STR test, and I originally
ordered 37-marker tests for these men.
The descendant of Michael Kern from Bedford did not
have any Y-DNA matches and did not appear to be related to the Michael of Knox,
but I need at least one more tester to be sure.
The Michael Karnes of Knox had several DNA matches, so we can find out more about him.
The Y-DNA results include a list of people who closely match your STRs. Below is the list of matches for one of the descendants Michael Karnes of Knox County. This man's surname is now spelled Karns.
The Y-DNA results include a list of people who closely match your STRs. Below is the list of matches for one of the descendants Michael Karnes of Knox County. This man's surname is now spelled Karns.
Mr.
Karns is not listed here; these are the people who match his Y-DNA. Notice the
spelling of the various surnames: Carnes, Kern, Karnes. There's even one Moreno, but he doesn't have a family tree. From DNA we know that all of these men are probably related.
 |
| Y-DNA STR Matches |
The genetic distance in the first column gives us a clue to how closely related these men are. The first man on the list is the other descendant of Michael Karnes. After ordering the initial test, I ordered a SNP test for him and upgraded his STR test to 67 markers.
Family Tree DNA shows what tests were taken by each man. For example, the fourth man on the list has tested 111 markers, has taken the Family Finder (FF) test, and the Big Y test.
If Mr. Karns took the Family Finder test, these men may not be on his list of matches because they may not share any autosomal DNA segments with him.
This is one reason that Y-DNA is so powerful--Y-DNA is passed relatively unchanged with each generation and does not get broken up like autosomal DNA segments do.
As I was looking through the above DNA matches, I noticed
that one Kern was descended from Adam Kern of Frederick County, Virginia.
Genealogical research from DNA clues
The earliest record I could find of Michael Karnes
was a 1766 deed in Frederick County, Virginia.
In 1773 Michael left Frederick County and
had deeded some of his land to a man named Adam Kern. Adam's name is showing up as a Y-DNA match, so now I decided to get all of
Adam’s deeds to see what I could find.
As it turns out, Adam split that land into several parts, and in one
significant 1796 deed to his first son Nicholas [Frederick County,Virginia, Deed Book 24B, page 565] Adam stated that he
received this land from his brother Michael.
I started crying. It
had long been believed that Adam might have a brother named Henry, a brother
named Michael, and a brother named Nicholas, but nobody had ever determined the
exact relationships.
I traced the
children of all four men and noticed that Michael, Adam, and Henry had each named
their first son Nicholas. So I decided that all family trees were likely incorrect,
and that these men were probably sons of a man named Nicholas.
I checked the list of DNA matches again. Although all the men had family trees there was no common ancestor, so I traced the lineage of the men on the list.
In addition to the
two men whom I know are descended from Michael, two men on the DNA match list
are descended from Adam, and one is descended from Henry. The lineage of one
man is still uncertain.
Adam Kern had married in York County, Pennsylvania shortly
after coming to Frederick County, Virginia, so I went looking for a man named
Nicholas in York County. I found him, and knowing
the names of some of his children, I was actually able to trace the entire
family to their hometown in Germany.
The German origins of Michael Karnes (Kern)
Johann Nicolaus Kern married Maria Apollonia Spicker 13 Feb
1738 in Flonheim, Germany. The marriage record stated that the father of Nicolaus was Nicolaus Kern, deceased, from Erbes-Bűdesheim, and the father of Maria Apollonia was Hermann [sometimes spelled Hermanes] Spicker of Flonheim.
Johann Nicolaus and Maria Apollonia Kern had the
following children baptized in Flonheim. I will show images for the first three
men, because our DNA testers are descended from them:
Johann Henrich Kern, 7 Aug 1740
 |
| Baptism of Johann Henrich Kern |
Johann Adam Kern 26 Mar 1742
 |
| Baptism of Johann Adam Kern |
Johann Michael Kern 7 Jul 1744
| Baptism of Johann Michael Kern |
Johann Nicholas Kern 5 Jun 1746
Johann Georg Kern 12 May 1748
Johann Paul Kern 2 Oct 1749
The Kern family in America
The Kern family left Germany and went to America to join Maria Apollonia’s
family. Her parents Hermann Spicker and
Maria Ursula Brűcker went to Pennsylvania and arrived 15 Sep 1749 on the ship
Edinburgh.
Nicholas and Maria Apollonia Kern took the same ship two years later
and arrived in Philadelphia 16 Sep 1751. It must have been a miserable trip for
Maria because she gave birth in York County the next month. They had the
following children baptized in York County, Pennsylvania:
Maria Magdalena Kern 11 Oct 1751
Carl Kern 1 Apr 1753
John Kern 21 Sep 1754
John Kern 2 Sep 1756
Anna Maria Kern 2 Sep 1756
Henry Spicker [brother of Maria Apollonia] and Maria Ursula Spicker [mother of Maria Apollonia] were witnesses to the baptism of Carl Kern in 1753. The Kerns and Spickers were on multiple documents together in York County, Pennsylvania.
The Kern family moved to Frederick County, Virginia, about
1765. Nicholas Kern [spelled Carn on the administration bond] died that year,
and his wife Mary was appointed administrator. Her son Henry Carn [the signature is spelled Henrich Kern] and brother Julius Spicker signed the administration
bond.
 |
| Administration bond for Nicholas Carn |
These Kerns do not yet appear to be related to any other Kern
family in Colonial America.
Learning more from Y-DNA
I notified all of the men on the Y-DNA matches list about my new
findings, and here is a portion of how they currently appear in the Kern surname project:
| Kern surname project at Family Tree DNA |
By comparing the Big Y results of the two men who have tested, we can begin to learn more about the Kern lineage.
Haplogroups and SNPs
Before we examine the Big Y results, notice in the above screenshot for the Kern surname project that STR results indicate that the men are related, but these STRs are not enough to distinguish between the various lineages.
Now look at the third column. The third column is for haplogroup. A haplogroup is a group of people who are related genetically and share a common ancestor.
These haplogroups seem to be very different and can make it look like these men are not related. But they are!
The haplogroups in red are predicted haplogroups. This means that Family Tree DNA looked at the STR patterns of these men and predicted that they belong to haplogroup J-M172.
J-M172 is an ancient haplogroup that has been estimated to be between 19,000 - 24,000 years old. We are not going to be able to determine the name of our common ancestor that far back!
We can get closer in time by ordering something called a SNP test. I did this for one of the men, and he was confirmed to be in haplogroup J-Z1296. His haplogroup is colored green which indicates that it is not merely predicted; it has actually been confirmed with a SNP test.
J-Z1296 is a branch of J-M172. Yfull.com estimates J-Z1296 to be about 4500 years old. That's much closer in time, but still not useful for genealogy.
So we need to discover new SNPs that can bring us into the genealogical time frame. That is the purpose of the Big Y test.
Now look at the two green haplogroups J-BY45500. This haplogroup is brand new. Haplogroup J-BY45500 was discovered with the Big Y tests of these men.
EXAMINING BIG Y RESULTS
Matching
Matching
The Big Y test can find SNPs that have never been discovered. It can take your haplogroup from an ancient time period to a more modern one, and even find SNPs that only you have.
When we get our Big Y results we should first look at the Matching tab. We will see our new haplogroup displayed along with a list of matches. The haplogroup of Mr. Karns is reported as J-Y98609, and he has only one match--a Mr. Carnes.
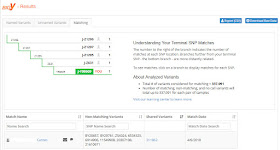 |
| Big Y Matching |
This is where I could get depressed and say, "I only have one match, and my haplogroup didn't change much. What a waste." But this is just the beginning of the process.
Next to the name of the match, there is a list of Non-Matching Variants. The Non-matching Variants are the SNPs that are not shared between the two men. You will want to compare this list to the list of Unnamed Variants
Unnamed Variants
Many people have misinterpreted the Unnamed Variants and have assumed that these are private SNPs not found in anyone else.
According to FTDNA, however, "The Unnamed Variants tab displays your SNP markers that are not on the list of ~70,000 known SNPs. These markers may or may not be unique to you as an individual. Men in related lineages may share some Unnamed Variants."
This means that in the Big Y process all previously-unnamed SNPs that are found in your results are automatically put into the Unnamed Variants section even if these SNPs are shared with another tester.
Newly-discovered SNPs that are shared between two men will be given a name by Family Tree DNA. However, the naming of new SNPs is not automated, and the initial results will require a manual review. It usually takes at least a week for the results to be finalized.
When you first get your results and click on the Unnamed Variants tab you may see a long list of unnamed variants. Compare this list to the list of Non-Matching Variants in your Matching tab.
The Unnamed Variants that are not in the Non-Matching Variants list may be shared with your match. In the screenshot in the section above, there are eight Non-matching Variants [BY28657, etc], but there are many Unnamed Variants:
Again, it may take awhile for the manual review process. You might want to take a screenshot of the Unnamed Variants list and a screenshot of the Non-Matching Variants results because these will probably change during the FTDNA review.
Family Tree DNA will name any matching SNPs, create a new haplogroup, and maybe even remove a couple of variants from the list.
After the Big Y manual review
After the Big Y results of the two kits have been compared and reviewed by Family Tree DNA, we actually have results we can work with. Here is the new haplogroup:
 |
| New haplogroup from Big Y results |
The haplogroup is now reported as J-BY45500. We still have one match at each of the five haplogroup levels. We need to review what we are really seeing here and understand that these results are fantastic! Here are the important points:
1. We need to know why there is only one match. If I click on the person icon next to Haplogroup J-Z1297, I will see that person's results.
In this case, I see the same name (Carnes) at all levels. Does this mean that only one other person has tested positive for SNPs J-Z1297, J-Z1295, J-Z631, J-Y98609, and J-BY45500? Absolutely not. Family Tree DNA will only display matches who have no more than a 30-SNP difference with you.
If someone is not related within 30 SNPs, they are probably not related within at least a thousand years.
So here's the first good news--I'm not going to waste my time trying to find the names of common ancestors when it will not be possible. I can look at the haplogroup projects if I want to see distantly-related people.
2. There has to be at least one more person at haplogroup Y98609, otherwise these two Karns/Carnes men would not have formed a new haplogroup under it. The other men who share haplogroup Y98609 cannot be within 30 SNPs of Mr. Karns, or they would be on his match list.
3.Since there is only one match at five haplogroup levels, Mr. Karns must share several SNPs with this person because they both share all of those five SNPs, and possibly more.
4. The "terminal" haplogroup, J-BY45500 is not actually final. It is the last SNP, or group of SNPs, that is shared between these two people.
Mr. Karns had several unnamed variants that Family Tree DNA has now named and placed on the human haplotree.
In a final group of SNPs, there is no way to determine the order in which they occurred. Family Tree DNA chooses one of these SNPs as the haplogroup designation and groups the rest of the SNPs with it.
When other testers in the future have some of these SNPs, but not others, Family Tree DNA can then decide the order of the SNPs, and new haplogroups will be formed.
In addition, when a future tester shares one or more of your unnamed variants, your haplogroup will be further refined.
5. If there is nobody else within 30 SNPs, we have just uncovered new SNPs and made a great contribution to science and to family history.
Doing our own evaluation of Big Y results
Let's find out how many SNPs are shared between Mr. Karns and Mr. Carnes. Click the myFTDNA tab, Y-DNA, then click Haplotree and SNPs.
 |
| Haplotree and SNPs |
You will be taken to your exact position on the human haplotree. Your haplogroup will be highlighted in green.
Click "More" next to BY45500 to see a list of other SNPs. In this case we see 12 SNPs in addition to BY45500.
Since Mr. Karns has only one DNA match in his newly-created haplogroup BY45500, the two men share these 13 SNPs.
 |
| Confirmed haplogroup with SNPs |
We can see the details of each of these SNPs by using the Big Y chromosome browser. From your Big Y Results screen click the Named Variants tab, and enter the name of the SNP in the SNP Name Search box.
 |
| SNP Name Search |
When the SNP name appears under the search box, click the link to see this SNP in the Y-Chromosome Browsing Tool.
 |
| SNP Name Search for BY45501 |
From the Y- Chromosome Browsing Tool we can find details about SNP BY45501. It is Position 8005382. The Reference Sequence has a T in this position, and Mr. Karns has a G.
 |
| Chromosome Browser |
Because it is now named, position 8005382 should no longer appear on the list of Unnamed Variants. We can look up each named SNP in the chromosome browser and see its details. There are 13 total named SNPs, but Mr. Karns originally had 21 unnamed variants.
Since 13 SNPs have been named we might now expect to see eight Unnamed Variants. However, in his new list of Unnamed Variants Mr. Karns now has only four.
FTDNA names SNPs when they are shared with someone else. Since these mutations are not shared with Mr. Carnes, these all probably occurred in the line of Michael Karnes and his descendants.
We can know exactly in which generation each mutation occurred by testing more descendants of Michael.
There are now 13 shared SNPs and four "private" SNPs (the unnamed variants that remain for Mr. Karns). But originally there were 21 unnamed variants. What happened to the other four SNPs?
We can use the Y-chromosome browser at ybrowse.org to look up the four positions and see that these SNPs had already been named and should not have appeared on the list of "unnamed variants." Here is one of them:
 |
| Details for position 15274092 |
This position had already been named A5563, but was not on FTDNA's list of named SNPs. The SNP name was found during the manual review.
By examining each position from our screenshot of the previous list of Unnamed Variants, we can know what happened to all 21 unnamed variants during the Family Tree DNA review and know the full set of shared and unshared mutations.
I contacted the person who manages Mr. Carnes account and asked what his unknown variants are. He has five of them.
If at least one of these mutations did not occur in any of the descendants of Nicholas Kern (1715-1765), Mr. Carnes could be a more distant relation.
The amazing power of Y-DNA
- I used Y-DNA to solve a decades-long mystery about my mother's mother's mother's father's mother's father's father's father--eight generations back, weaving between maternal and paternal lines. All we have to do is find a direct paternal descendant of any of our ancestral lines and do a Y-DNA test.
- Because of the clues from Y-DNA STRs, we now know the exact lineage of all of the matching Kerns except for one. Each of these lines has been extended multiple generations back to its German origins. The STRs were not enough to help pinpoint the ancestral line of Mr. Carnes, but he does know that he is related to this group of German Kern men and is not related to men from Ireland, for example, who may have spelled their name Cairns.
- STR results were enough to help me trace the origins of my ancestor Michael Karnes back to Europe, but the SNPs in the Big Y test did even more. Even though we may never be able to know names such as Johann Kern for generations further back, I can use the Haplotree and SNPs screen to see that I have ancestors who have been given the names BY45500, Y98609, Z631, and so on, all the way back to "Y-Chromosomal Adam." Genealogy doesn't get better than that.
- Mr. Karns and Mr. Carnes share 13 SNPs that have not been seen in anyone else. The two men are definitely related. These 13 SNPs have now become part of the human haplotree and will be available for family historians and scientists. Because we know the geographic origins of this family, we will eventually be able to assign at least one of these SNPs to a precise location.
- Mr. Karns has four, and Mr. Carnes has five unnamed variants. These mutations occurred in their own family line and not in the line of the other man. These unnamed variants can be named and tied to specific ancestors by testing more Kerns descendants. When any of these unnamed variants is found in another man, a new haplogroup will be formed.
What can we do next?
1. YSeq: Submit the named SNPs and the unnamed variants to the Wish-a-SNP program at YSeq so that anyone can test one or more of these SNPs.
2. YFull: In many haplogroups, including the J2 haplogroups, further evaluation by YFull is highly encouraged. One good reason for this is to further preserve your results. Are there any other good reasons? Will YFull tell us anything further? See Advantages of submitting to YFull.
3. STR upgrades: Encourage current Kerns Y-DNA testers to upgrade their STRs to 111 markers. There are three differences in the 68-111 marker panel between Mr. Karns and Mr. Carnes. Seeing these in the tests of the other men will help to verify the lineages.
4. Big Y Upgrades: Encourage current Kerns Y-DNA testers to consider taking the Big Y test.
Encouraging more Big Y testing is especially important for Mr. Carnes because he does not know where he fits into this lineage, and he has five unnamed variants.
If some of these unnamed variants show up in the Big Y tests results of other men whose lineage is known, his own lineage will be obvious. If they do not show up, it could indicate that Mr. Carnes is a descendant of another son of Nicholas or even one of the brothers or other relatives of Nicholas Kern who could have immigrated to America.
Each man taking the Big Y test will verify his lineage and discover the private SNPs that occurred in his own Kern line. He will be able to determine the exact ancestor in whom each SNP occurred by testing more relatives.
5. New testers: Encourage new Kerns men to take a Y-DNA test. The more data we have, the better.
For example, Nicholas (the brother of Henry, Adam, and Michael) has known descendants, and their DNA has not yet been tested. This step will be critical to Mr. Carnes if the Big Y test results of current Kerns testers don't match his.
By testing more men with the Kern surname, maybe I'll even be able to find the father of my other ancestor Michael Karnes!
6. SNP packs: Work with a haplogroup administrator to get some of these newly-discovered SNPs into one of the Family Tree DNA SNP Packs so that they are easily available for testing.
7. New STRs: I was going to write that we've gone as far as we can go with Family Tree DNA until someone else decides to do further Y-DNA testing, but then I noticed that there were pending DNA test results.
I clicked on the above link and I saw this:

In November 2017, Family Tree DNA announced that in 2018 they would be including about 500 STRs, in addition to the SNPs, in Big Y results. These would not just be for new Big Y testers; anyone who had ever taken a Big Y will see them. There will be no additional charge for these new STRs. While there is no expected date, it is obvious that the "Y500" is now in the pipeline. Ahhhh, the gifts just keep on coming.
See the incredible update here: STRs now included in Big Y500 test!
Summary
Y-DNA can focus on a specific lineage and do what no other DNA test can do. If you have not yet started Y-DNA testing in your family, please consider it.
Each DNA test helps not only you but others as well. I would not have been able to achieve this incredible breakthough if other men had not taken a Y-DNA test.
The Y-chromosome is carried only by men, so only men can take this test. Remember, though, that you can use Y-DNA of cousins and other more distantly-related men for any of your ancestral lines.
Every year there is a DNA Day Sale in the month of April. See Announcing Family Tree DNA's new Big Y-500 test.
With the new Big Y-500 you will get not only recent, newly-discovered SNPs, but you will know your decent all the way back to "Y-Chromosomal Adam." In addition, you'll be getting a complete 111-STR test and new STRs giving you at least 500 total.
You can use the amazing power of Y-DNA to help your own family history research as well as preserve a story about your family for future generations.
Update: Were the these men related: Michael Karnes of Bedford and Michael Karnes of Knox. We now have the answer! See Y-DNA testing for Genealogy: Are these men related?
______________________________________________________
Disclosure
Links to Family Tree DNA appear in the sidebar. I receive a small contribution if you make a purchase, but clicking through the link does not affect the price you pay.



Excellent blog. I envy your genealogy work to find those records to then lead to testing your hypotheses. I've tested my first immigrant from Ireland (c. 1779) using myself and descendants of other sons of this first immigrant. Still no closer to figuring out who his father was however, except for finding matches and creating a new SNP across 3 of us dated to around the 1600s.
ReplyDeleteHi Linda Some time ago, I discovered my autosomal DNA connection taking me back to Michael Karnes/Kerns. I noticed a discrepancy for the wife's name, since there were two Michael's. Then I was able to find my DNA match to Persinger, and for some matches I'm matching both Kerns and Persinger with one DNA match on two chromosomes. One of my 3rd Great Grandmother's was Christena Carnes who married Andrew Cowan Jasper in KY. Her parents were Abraham Kerns and Elizabeth Frederick. Michael Kerns and Elizabeth Persinger were my 5th Great Grandparents, and I was somewhat surprised that I have pretty good matches going back that far. My matches for the two surnames of Kerns/Karnes/Carnes and Persinger are on chromosome 4 and chromosome 17. It appears I may be matching someone you manage that matches me on the area of chrom 17 I mentioned. Thanks!! Tom McMillan
ReplyDeleteTom McMillan, Please contact me through the contact form.
ReplyDeleteIts amazing scinces
DeleteThank you. I especially like how yyou used yDNa and documentary research to support each other. This lineage has parallels to my paternal grandmother's Cales lineage -- also of Germanic immigration in the 1740s and also haplogroup J.
ReplyDeleteLove your post. It has helped me understand more of my Big-Y500 results! Thank you. Hopefully I can make more sense of I-Y139066 that belongs to myself and our oldest son! Of course trying to see where the other Chambers families are on the Family tree also. Have one more Big-Y500 being processed at FTDNA and one more being looked at by Y-Full.
ReplyDeleteThank you for this education! My husband has three DNA matches to descendants of George Karnes/Kerns, Sr (b ca 1741) of VA's sons--but what a tangled mess folks have made, trying to trace back that line. I'm a Y DNA newbie, so here's my question: Why are we getting Y DNA matches at 37 markers to both Irish and German Karneses?
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteGeorge Karnes is supposed to be the brother of Michael Karnes who died 1807 in Bedford County. They were definitely German. Please contact me through the blog contact form so that I can help you with this.
ReplyDeleteLinda,
ReplyDeleteI have sent you an email. Please look at it. Thank you.
Angie Kerns Wendt
Thanks a lot for your lovely blog post.
ReplyDelete"I now know where each man lived and have determined the children of both men." I am curious as to what names you have for their children. I believe I am related to Michael of Bedford but I'm not sure. An Elizabeth Kern/Karn married a Joseph Clark in Bedford County on 25 Feb 1793. I think this is Michael of Bedford's daughter.
ReplyDeleteAaron Clark, Elizabeth Kern (who married Joseph Clark) was the daughter of Michael of Bedford.
ReplyDelete